Imagine a world where digital information seamlessly blends with reality, enhancing everyday experiences. Wearable augmented reality (AR) is at the forefront of this technological revolution, transforming how people interact with their surroundings. From smart glasses to AR headsets, these devices are not just gadgets; they’re gateways to a new dimension of information and connectivity.
As industries like healthcare, education, and entertainment embrace wearable AR, the potential applications are limitless. Users can access real-time data, receive interactive guidance, and immerse themselves in engaging content—all while staying connected to the physical world. This fusion of digital and physical realms is reshaping how individuals perceive and interact with their environment, paving the way for a future where the lines between virtual and reality blur.
Overview of Wearable AR
Wearable augmented reality (AR) devices enhance experiences by overlaying digital information onto the real world. Smart glasses and AR headsets represent the forefront of this technology, enabling seamless interaction between virtual content and physical environments.
What Is Wearable AR?
Wearable AR integrates digital elements into a wearer’s view of the real world through devices like smart glasses and headsets. These devices utilize displays, cameras, and sensors to project information, enhancing surroundings with relevant data and interactive features. Applications span various sectors, including healthcare, where surgeons access critical information during procedures, and education, where students explore immersive learning experiences.
Key Technologies Behind Wearable AR
Wearable AR relies on several key technologies that enable its functionality.
- Displays: Optical waveguides and microdisplays project images directly into a user’s field of vision, allowing for seamless integration of digital information.
- Sensors: Accelerometers, gyroscopes, and depth sensors gather data about user position and movement, enabling accurate tracking of interactions within real-time environments.
- Cameras: Forward-facing cameras capture the environment, facilitating object recognition and scene understanding, which enhance user interactions.
- Processors: Advanced CPUs and GPUs process large amounts of data to deliver smooth graphics and low-latency responses during user interactions.
- Connectivity: Bluetooth and Wi-Fi facilitate communication between wearable devices and other smart technologies, enabling data sharing and cloud connectivity.
Applications of Wearable AR
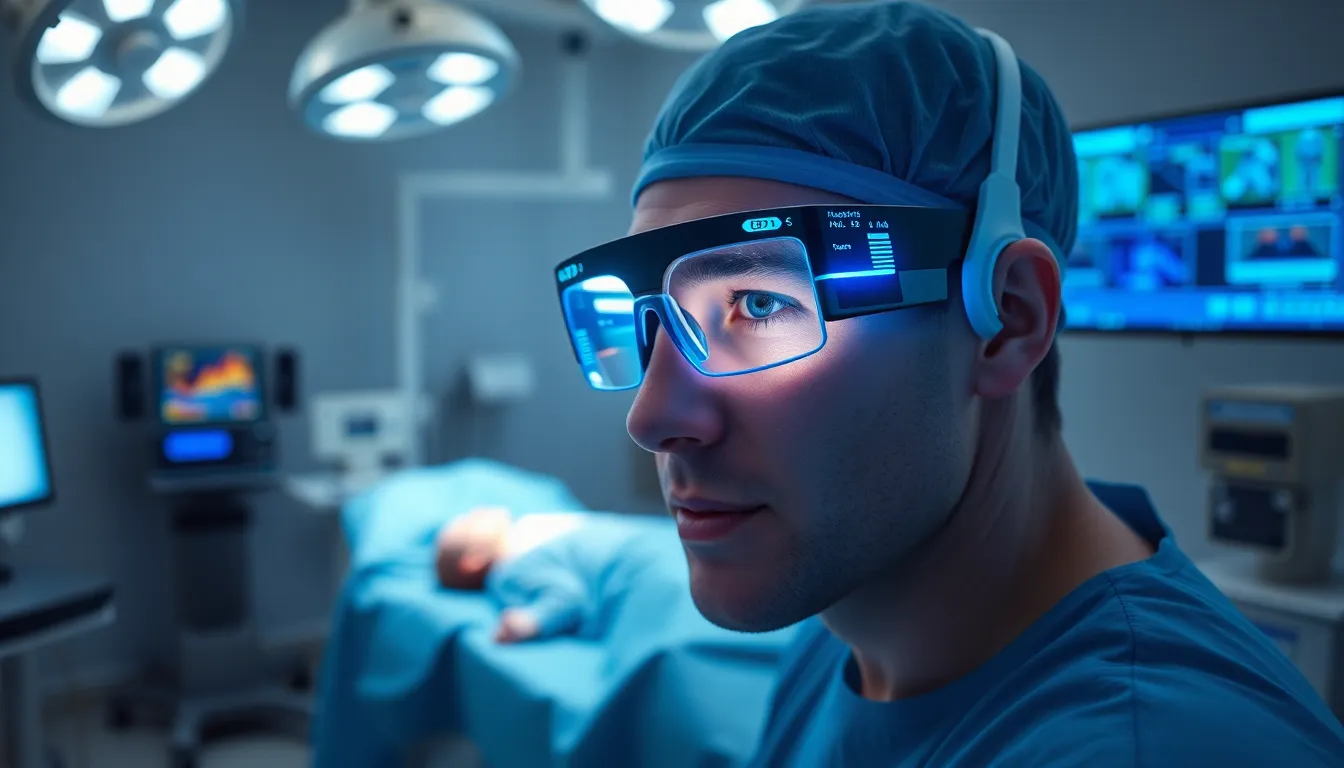
Wearable augmented reality (AR) presents transformative applications across multiple sectors, enhancing functionality and improving user experiences. Below are key areas where wearable AR technology creates meaningful impacts.
Healthcare
Healthcare professionals use wearable AR to enhance surgical precision and procedural efficiency. Surgeons wear AR glasses to overlay vital patient information during operations, reducing the need for physical charts. Such integration improves accuracy in complex procedures by minimizing distractions. Medical training also benefits, as students observe live surgeries with interactive elements detailing anatomy and techniques, improving learning outcomes.
Education
Wearable AR fosters immersive educational experiences that engage students more effectively. In classrooms, AR devices overlay digital content on physical environments, allowing students to visualize complex concepts, such as historical events or scientific processes. For example, students can explore 3D models of the solar system, enhancing comprehension through interactive learning. Additionally, remote learners gain access to virtual field trips, providing diverse educational experiences unavailable in traditional settings.
Retail and E-Commerce
Retailers leverage wearable AR to improve customer engagement and streamline shopping experiences. Smart glasses allow shoppers to visualize how products fit into their lives, such as trying on clothes virtually or visualizing furniture in their homes. E-commerce platforms also use AR to help customers preview products, increasing confidence in purchasing decisions. This technology leads to higher satisfaction rates and reduced return rates, benefiting both consumers and retailers.
Advantages of Wearable AR
Wearable augmented reality (AR) offers several compelling advantages, enhancing both user interaction and productivity across various sectors.
Enhanced User Experience
Enhanced user experience manifests through immersive interaction and intuitive interfaces. Wearable AR devices provide real-time feedback by overlaying digital information onto the physical environment, creating a seamless interaction layer. Users can visualize data, enabling more engaged learning and informed decision-making. In retail, for instance, shoppers can view product specifications and virtual try-ons, improving satisfaction and reducing return rates. In healthcare, professionals access vital information during procedures without interrupting their workflow, leading to smoother and safer operations.
Increased Productivity
Increased productivity results from streamlined workflows and improved access to information. Wearable AR facilitates multitasking, allowing users to perform tasks while receiving vital information. For instance, factory workers can receive instructions and track inventory levels through AR glasses, minimizing downtime and errors. In the field of education, students using wearable devices gain instant insights, enabling deeper understanding and promoting efficient study habits. Overall, wearable AR tools significantly contribute to enhanced efficiency and performance in various professional environments.
Challenges and Limitations
Wearable AR faces several challenges that hinder widespread adoption and usability. Key areas of concern include technical limitations and privacy and security issues.
Technical Limitations
Technical limitations of wearable AR devices significantly impact performance and user experience. Battery life remains a critical challenge, with many devices struggling to last a full day under heavy use. Display technology also presents constraints; current screens often fail to deliver the clarity and brightness required for effective outdoor use. Processing power is another limitation; many wearable devices lack the capability to handle complex applications in real time, leading to lag and reduced functionality. Additionally, issues with field of view and tracking accuracy can hinder the seamless integration of virtual elements into the real world, resulting in disorientation for users.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Privacy and security concerns pose significant obstacles to the adoption of wearable AR. Given the continuous data collection from devices, users face risks related to unauthorized access to personal information. The potential for misuse of camera features can lead to surveillance and data breaches. Additionally, companies that develop wearable AR must comply with regulations surrounding data privacy, which can complicate application development and deployment. Ensuring user consent and data protection becomes essential to build trust and promote widespread acceptance of these technologies.
Future Trends in Wearable AR
Wearable AR technology continues to evolve, leading to significant advancements and market growth. As it integrates more into daily life, emerging technologies and potential market growth play crucial roles.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies enhance the functionality and capabilities of wearable AR devices. Miniaturization of components enables lighter, more comfortable devices. Advances in optical waveguides improve display quality and create more immersive experiences. Additionally, integration of AI provides context-aware content, resulting in personalized user interactions. Cloud computing empowers real-time data processing and increases the availability of complex applications without relying heavily on device hardware. Improved battery technology extends usage time, addressing a key limitation in portable AR devices. Ongoing research in haptic feedback enhances user interaction, making experiences more tactile and engaging.
Potential Market Growth
The global wearable AR market is projected to grow significantly over the next decade. According to industry reports, the market is expected to reach $61 billion by 2028, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 29%. Factors driving this growth include increased demand from sectors such as healthcare, education, and retail. Enhanced user engagement, improved performance, and evolving consumer preferences also contribute to expanding adoption rates. As major companies invest in AR development, competition fosters innovation, leading to more diverse and advanced wearable AR solutions. With continual advancements in technology and expanding applications, wearable AR is moving toward substantial integration in various sectors.
Wearable AR is on the brink of revolutionizing how people interact with their environments. As technology advances and applications expand across industries like healthcare, education, and retail, the potential for enhanced experiences is immense. While challenges such as technical limitations and privacy concerns remain, ongoing innovations promise to address these issues. The future of wearable AR looks bright with significant market growth anticipated. As companies continue to invest in this technology, users can expect more seamless integration of digital and physical worlds, ultimately reshaping everyday life and work.
